
- erfume and perfume water. Сosmetics
How to recognize a fake - Structure of shampoo
- Natural soap. The composition of natural Soaps
- The composition of toothpaste. Structure of cream
- Aromatic substances
How to strengthen the smell of perfume - Structure of shampoo
- Toilet soap. Making soap at home
- Ether oil
Getting a complex ether
Getting ether oil
Solve the tasks
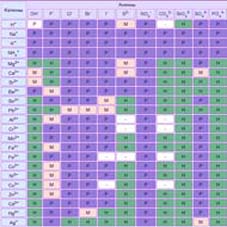
- Units of measure:
measure of length, measure of volume, measure of weight, measure of area - Heat capacity of liquid
Coefficient of thermal expansion - Chemistry tasks. Solve simple! Examples
- The density of substances (materials)
- Graphics solubility of salts in the water
- Chemical name
- Saturated hydrocarbons.
Homologous series

- Properties of acids. Getting acids
- Organic acids. Properties of carboxylic acids
- Acetic acid. Formic acid
- Nitric acid
- Sulfuric acid. Sulfurous acid.
Getting sulfuric acid - Hydrocyanic acid. Boric acid
Silicic acid - Hydrochloric acid. Oxygen-containing acids
- Carbonic acid. Phosphoric acid
- Amino acids. The properties of amino acids

- Artificial crystals and natural crystals
- Poisonous, toxic and explosive substances
- Poisons. Antidote
- Organic glass. Ceramics
- Liquid glass. Silica gel
- What is the enzyme. How do enzymes
- Using of enzymes
- Toxins and antidotes
- History of chemistry. The development of chemistry
- Mendeleev Dmitry Ivanovich

- Metals. Properties of metals.
Electrophysical property of metals - Metal corrosion.
Electrochemical corrosion - Bismuth. Chemical properties of bismuth
- Mercury.
Arsenic. How to detect arsenic - Pure aluminum, pure tin
Natrium. Titanium - Manganese. Metal uranium
- Nickel. Metal germanium
- Metal chrome. Vanadium
- Pure copper, pure iron
- Gold. Silver. Platinum. Ultrapure metals

- Complex substance. Water hardness
- Composition of matches. Incompatible substances
- Manganese. Hydrogen peroxide
- Ammonia. Properties of ammonia
- Hydrogen sulfide. Obtaining hydrogen sulphide
- Bases. Properties of bases. Lye
- Properties of oxides
Basic and acidic oxides - Phenolphthalein
- Protein. Properties of proteins
- Alcohols. Properties of alcohols
- Resin. Phenol-formaldehyde resin
- Solid grease. Liquid grease. Grease properties

- Ion exchange reactions. Neutralize acid.Hydrolysis
- Chemical reactions. Types of chemical reactions
- Chemical experiments
- Velocity of chemical reaction
- Qualitative reaction
- Indicator pH. Color of indicator
- Cooling mixture. Endothermic reaction
- Catalysts. Inhibitors
- Properties of catalysts. Efficiency of catalysts
- Enzymes. The action of enzymes
Entertaining chemistry is a natural science, which is descriptive examples, not going into the "wilds" of formulas and theories, shows and tells about the structure and the transformation of simple and complex substances.
Entertaining chemistry tells about the most interesting and useful properties of the substances. Illustrations and pictures presented on the website, allows us to see and get to know some common chemical compounds (for example, substances containing calcium and sodium).
Entertaining chemistry in an accessible form will give an explanation about pure metals, their alloys, complex and simple chemical substances, substances with high molecular weight compounds, that You often use at home.
All known manganese is a complex substance and has own distinct properties. To this class of substances is used by us in the kitchen - baking soda, in the bathroom - with washing soda (calcinated soda).
In nature, the majority of substances is a complex substances, that is formed during chemical reactions from simple substances. Without a doubt It complex substance, generaly, presents a variety of substances used on our planet today!
!
Simple substances or complex substances have individually defined property, which are divided into chemical and physical. We use them, without much thinking about it, using the properties of the chosen system in the mercenary purposes. For example, eat the food, that we like, because it has a certain acceptable to us taste, sweet - marked by the presence of sucrose and glucose, acid - marked by various organic acids, salt - salt, bitter - also by the presence of salt or chemical compound of another class. Chemical properties are shown in chemical reactions. Eating, we put food chemical reactions by which we feel its taste. Reactions, occurring on our tongue, also refer to the chemical. In addition, specific areas of tongue perceive a certain taste: the tip - sweet side part is salty and sour, closer to the base - bitter. Saliva contains 90% of water, other - mineral salts, with slightly alkaline reaction.
All chemistry is based on the 2 pillars: organic chemistry and inorganic chemistry. There are many similarities, but also many differences. Total enclosed in single laws transformations and interactions between substances (for example, organic acid - acetic and inorganic acid - salt, will have similar chemical properties to dissolve certain metals, react with salts, basic oxides and bases). The differences are, of course, and justified by the chemical structure each of them.
The knowledge base of inorganic chemistry lies in the following classes:
- acids, bases and alkalines, oxides, metals and nonmetals.
Knowledge of the basic properties of the main representatives of each class will make it easy to navigate in chemistry!
In resource Entertaining chemistry you will find all the basic properties of classes of chemical substances, presented in a descriptive way. Properties illustrated with drawings and explanations, interesting facts and descriptions.
Chemistry Of The Earth. The elements of our planet
It is safe to say that the Earth consists of all elements of the periodic table, but each element is mass part of our planet.
Oxygen O2 is the main and can say that one of the main elements of the Earth. Его процентное содержание по массе Земли составляет около 49,5%.
The next element by mass, is a silicon - Si. Its mass fraction is 25.3%. On the third place - aluminum - Al. He is 7.5% of the mass of the Earth. Next is the iron - Fe 5,1%, calcium - Ca -3,4%, sodium 2,6%, potassium - 2,4%, magnesium -1,9, hydrogen - 1,0%, titanium - 0,6%, carbon - 0,1%. The rest of the metals and non-metals are less than 0.1% of the mass Earth.
Atmospheric chemistry. What gases make up the atmosphere
Our atmosphere is shell, consisting of several layers, the total thickness exceeds 1000 km. There are no exact borders between layers . In order of removal from the surface of the Earth our atmosphere consists of: the troposphere (about 11...12 km), stratosphere (up to 45...50 km), the mesosphere (up to 85...95 km), the thermosphere (up to 600...700 km), the exosphere (above 800 km). the pressure in the atmosphere of gases decreases With increasing altitude (increas discharge).
The main part of the air, of course, concentrated in the lower part of atmosphere. Dry air is a mixture of gases and has the following volume ratio: nitrogen (78,095%), oxygen (20,939%), carbon dioxide (0,031%), inert gases (helium, neon, krypton, xenon, argon - 0,935%), from which is argon - 0,933%.
Chemistry person. The elements of our body
What do you think, how many different chemical elements in our body?! It turns out, 4 % of the weight of our body is minerals and microelementsthat is 81 chemical element of periodic table. These microelements come into our organism with food and posted by transport proteins in the zones of active metabolism or accumulate in our body. Each people needs microelements, they are used in the synthesis of useful organic substances and their mutual exchange. The absence of any of 81 trace element can cause serious health problems. But, of course, and surplus of not less harmful!
Let's consider a chemical element, for example, as bromine (Br). Bromine - known halogen (you can read more about it on the page nonmetals). Now, in small amounts this element is useful for the body. He is responsible for processes in the cerebral cortex: excitation and inhibition, is used as a sedative in pharmacy drugs, prevents moulds in foods (for example, in the bread). People get its mainly from sea food. On the other hand, bromine very poorly flushed and accumulates in the human's body. Here then are manifested all the negative properties on the body: rash, deterioration of sleep, loss of coordination of movements, nervous disorders. About a surplus bromineyou shouldn't worry, because, basically, it happens with people, who take medicine containing bromine (especially, if not on purpose!).
Heavy metals enter to our body through the air. These include cadmium, lead, etc. All, probably, have noticed the difference in the air near the city's roads and somewhere in the parks. Plants, fruit growing near road, railway stations, absorb with air these metals and can be harmful for humans when they eat it. For example, lead locks the beneficial effects of zinc for the body, disrupting the immune system, skin health, the digestive organs.
Microelements, wthat contained in aerosols, also enter in your body, for example, aluminium: its excess is blocking the positive effect of trace elements magnesium, responsible for health and the work of the heart and vessels!
Therefore, taking drugs with minerals, you need to maintain the balance it in the body. Then they will bring a positive effect!
- The color of gold is different (blue, red...)
- Useful substances in food
- Methods of preparation of invisible ink
- Why soap cleanses
- How to determine the shelf life of food
(and other useful tasks in chemistry) - What determines the color of the glass
- What's different?! ammonia and ammonia and ammonia
- Why fruits become brighter when ripe?!
- What is the vulcanization
















 Go to Russian
Go to Russian