Amino acid
Amino acid - these are derivatives of hydrocarbons that has two types of functional groups: carboxyl group has acidic properties and amino group has basic properties of this substance.
The general formula of amino acids: NH2-R-COOH.
Examples of amino acids can be:
- Aminoacetic NH2-CH2-COOH
- Aminopropionic NH2-CH2-CH2-COOH
- Aminocaproic NH2-(CH2)5-COOH
- Aminoenanthic NH2-(CH2)6-COOH
- Aminobenzoic NH2-C6H4-COOH
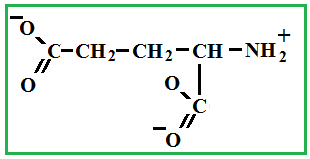
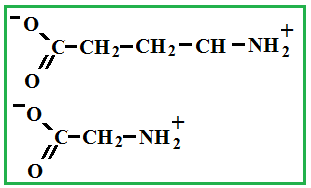
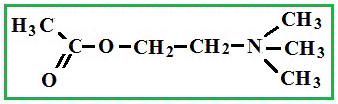
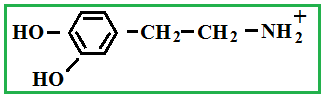
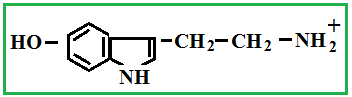
Depending on the location of these functional groups are many isomers. Of greatest interest is A-amino acids, i.e. amino acids, in which carboxyl groupand amino group are beside. It A-amino acids are part of proteins!
Amino acids - these are solid crystalline substances, which is explained with the structure of their molecules (inside each molecule there is an internal salt, where the salt is from a chemical point !).
Amino acid production
Amino acid production associated with hydrolysis proteins, but they can be synthesized from carboxylic acids, for which first chlorinated acids are obtained, which are then treated with ammonia.
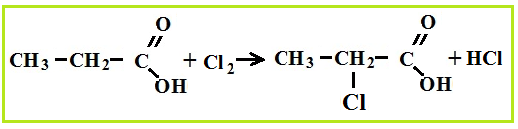
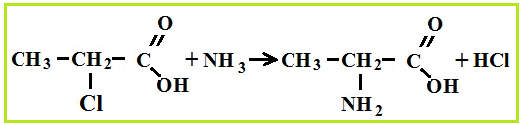
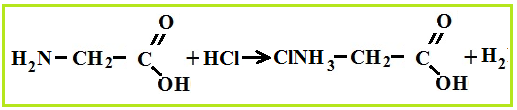
Amino acid properties
The presence of two opposite functional groups (carboxyl group and amino group) in amino acid molecules gives them amphoteric properties (properties of both acid and base). Thus, amino acids react chemically with bases and alcohols, thus forming chemical compounds similar to the reaction products of carboxylic acids with alkalis and alcohols - salts and esters.
As bases, amino acids easily react with acids and form salts.
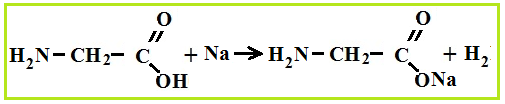
Amino acids can interact with each other, but this interaction is different from the usual reactions. As a result of the reaction, compounds with a large number of amino acid residues are polypeptides. The group of atoms-CO-NH is called a peptide group, and the bond between nitrogen and carbon atoms is a peptide bond or amide bond. Thanks to these bonds, amino acid residues are joined with protein molecules and some fibers (for example, in capron)
Amino acids as the "blocks" were built proteins, used in medicine: they prescribe to the sick and the strong and weakened after a serious operations and treatment in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, and nervous diseases. Amino acids are used in agriculture as an additive to animal feed.
Aminocaproic acid and aminoenanthic acid, used for feedstock for synthetic fibers "kapron" and "enant".
Aminopropionic acid - is formed by hydrolysis of natural silk. But it residue is contained in almost all proteins!
Aminoacetic acid - is a white crystalline substance that is very soluble in water. It has a sweet taste, so its second name is glycol.